To save your time, you can skip to the end of this article to go through a comparison table between Tor vs VPN vs Decentralized VPN so that an educated decision can be instantly made for your highest cybersecurity, anonymity, and privacy when using the Internet
Tor and VPN, What Differences between Them?
Tor and VPNs are both secure networking technologies designed to protect your online privacy or provide online anonymity. However, they are different to some extent. Is Tor better than a VPN service? Does Tor need a VPN? The differences between Tor and VPN will be discussed below.
What is Tor?
Deriving from a project aiming to protect Internet users since 2002, Tor is the name of an open-source browser, serving online anonymous communication. The term “Tor” is from the acronym of The Onion Router that is the name of the original software developed by Syverson and computer scientists Roger Dingledine and Nick Mathewson. Tor is an easy-to-remember name because of its “onion” icon indicating its multiple layers of encryption.

How does Tor Work?
The essential aim of Tor lies in privacy and anonymity. As a browser, your Internet traffic is led to different nodes administered by some people or devices so that websites can be anonymously visited. Moreover, your Internet traffic won’t be tracked because encryption is implemented on each node with your source IP addresses well hidden.
Based on a system originally developed by the US navy to protect intelligence communication, the Tor browser “cuts” your Internet traffic into smaller data encryption packages that are then routed through a huge node network. Anyone is allowed to run the nodes. Your data will be transmitted along randomized paths and pass at least 3 relay nodes before reaching the endpoint.
Each time your data passes a relay node, an encrypted layer will be removed, indicating the Internet traffic should be sent to the next relay node. Each relay node only unencrypts sufficient data so as to recognize the location of the next relay node. However, the exit node deletes the last layer of encryption and fails to monitor your location or IP address. If you visit an insecure website, however, the exit node will be able to see your online activities.
What does Tor Allow You to Do?
Anonymously Visit Websites
Tor can guard you to visit any website and any of your online traces won’t be left on your device or website servers as web browsing with Tor because it hides your IP address. This feature of Tor is similar to that of a VPN, at least from the name alone. A Tor can be used as a VPN when it comes to anonymous visiting online.
Visit Dark Web
This is the special feature Tor carries. Tor Browser can be used to visit the dark web, also called .onion domain, that fails to be reached through other browsers like Chrome. Although the dark web is usually related to crimes, it’s still useful when it comes to certain circumstances.
Securely Online Communicate with Others
Tor can be used for secure communication that is especially important for journalists, informers, politicians, or crime victims expecting anonymity. Tor stops their communication from being tracked or monitored, ensuring their total online security.
Unblock Geo-restricted Content
Tor allows you to access geographically restricted websites and content on the Internet. Similar to a VPN, Tor can be also used to bypass geo-restrictions for free browsing.
Allow You to Free Download and Use
Similar to most browsers, the Tor browser can be both downloaded and used for free and it supports multiple devices and operating systems. Quite easy to use.
What are the Disadvantages of Tor?
Attracting More Attention and Monitoring
To use Tor for web browsing, you need to access and exit relays that are public. Therefore, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and other third parties will be instantly aware that you’re using Tor. Even though they possibly fail to know what you’re doing or who you are on the Internet, the action of using Tor is worth doubting since Tor is always linked with crimes. Using a VPN minimizes outer attractions while using Tor, however, attracts more attention. That’s contrary to the purpose.
Low Connection Speed
Tor leads to a low connection speed because of its decentralized network that leads your Internet traffic to pass multiple nodes, which takes some time. Therefore, Tor isn’t sincerely suggested when it comes to video streaming or online gaming.
Still Can be Monitored
Some nodes can be still controlled by malicious people that can possibly monitor Internet users’ online activities by controlling sufficient nodes. Though the Internet fails to keep logs, users’ traffic or IP address can be possibly seen at the entrance and exit nodes. Scratch information can be still combined to be a sketch of a user.
Fails to Cover All Connections
The domain Tor can cover is only limited within the Tor browser. If you use another application or browser, it won’t be able to protect your cybersecurity or online privacy.
Run by Volunteers
All the nodes of Tor are used and run by volunteers so that they fail to be protected due to the absence of funds or responsibility.
Risk of IP Address Exposure
When you torrent using Tor or open the downloaded file through Tor, it’s risky for you to get your IP address exposed.
What is a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network also called a VPN, is a network service allowing Internet users to take advantage of the IP address of VPN servers to encrypt the connections between Internet users’ computers and VPN servers. An end-to-end encrypted tunnel is established by a VPN so that all the transmitted data between users’ devices and the Internet are completely encrypted.
Moreover, by connecting with the IP address of a VPN server at one place around the world, you’re also allowed to bypass geological restrictions or not to let others know about your real geological locations with your privacy well-protected.
To better understand what is a VPN, you’re suggested to directly skip to this non-technical beginner’s guide to understanding a VPN.
What Can a VPN Do for You?
Hide Your IP Address
As you get your device connected with a VPN server, your real IP address will be immediately masked by the connected IP address so that your device will be avoid being snooped by prying eyes like ISP, government, or any malicious third party.
Visit Restricted Content
A VPN can do as Tor does in unblocking restricted online content. As your device gets connected with a VPN server located in a place around the world, it’ll be disguised to be accessible to the Internet at a place where your targeted content is unrestricted so that your requests to visit the online content will be allowed. Therefore, it means a VPN can be used to unblock restrictions when streaming on Netflix or gaming online.
Establish an End-to-end Encryption Tunnel
As a VPN is used as you use the Internet, your request will be sent to remote VPN servers remotely located. On the VPN servers, requests are then sent to the Internet after decryption. When the website sends the information back to your device, the request will be directed to go through the encrypted tunnel as well so that encryption is implemented to your data before it arrives at your device. That means your messages won’t be exposed to prying eyes because they’re encrypted while they can be read by you since they have been decrypted when arriving at you.
Accelerate Connection Speed
Actually, using a VPN doesn’t essentially bring forward high connection speed while it’s able to avoid ISP limiting your bandwidth and data throttling because it’s beyond the reach of ISPs. Compared with the Tor browser, a VPN leads to a higher connection speed than Tor since a traditional VPN leads your device to the Internet after a VPN server connected but the Tor browser must pass multiple nodes, taking more time to reach the Internet.
Protect Security from Head to Toe
As long as a VPN is connected, all the data generated on your device and all the contacts between your device and the Internet will be well protected in the encrypted tunnel established by the VPN so that all browsing activities on any website and all your activities on the applications installed on your devices will be well protected. A Tor browser, however, only protects the communications occurring on the browser, with those on other browsers and applications excluded.
Customize Your Security Mode
A VPN can have advanced features to let users deepen and customize their security mode. For example, some VPNs have a kill switch that can directly cut Internet access once the VPN drops by accident. Or some VPNs set a split tunnel to direct partial traffic to go through the VPN encrypted tunnel and partial traffic to avoid it. As such, users’ local life won’t be affected even when a remote VPN server is connected.
VPN vs Tor, Which is Better When it Comes to Online Security and Privacy?
Based on the features of Tor over VPN, Both VPN and Tor browser have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Pros and Cons of Tor
Pros of Tor include:
- It’s impossible to track the visited resources from your IP address.
- The network is distributed or decentralized, so it’s difficult to close it.
- Tor is free to use.
Cons of Tor include:
- Tor features a low connection speed due to the fact that traffic passes through multiple network nodes.
- Many providers block Tor’s nodes on their network.
- Traffic on the last node is not encrypted, so personal data is accessible to third parties in the last node.
- The use of torrents is not allowed on Tor.
Pros and Cons of VPN
Pros of VPN include:
- VPN is easy to install and use.
- The connection is more reliable and the connection speed is higher.
- VPN features stronger encryption.
- You can run any network software-torrents, applications, email clients and all traffic will be encrypted.
- A VPN has a much higher level of confidentiality than Tor.
- Technical support is usually available whenever there’s an issue when you use it.
- Similar to the Tor browser, some VPN services can be used for free as well.
Cons of VPN include:
- Some VPN providers log users’ data and sell for profits.
- The centralized VPN features lower security and privacy compared with a decentralized VPN.
To sum up, the following conclusions can be made in terms of Tor over VPN.
- Tor is not a VPN and it’s just a browser. So, Tor can’t be used as a VPN.
- Tor can be used with or without a VPN. Working with a VPN, Tor can bring forward higher security.
- It’s impossible to say Tor is better than a VPN or a VPN is better than Tor because both of them have advantages and disadvantages.
Therefore, to achieve full-scale security, anonymity, and privacy, it’s optimal to use Tor with a VPN. As such, they can be a supplement to each other. Tor’s advantages can compensate for the disadvantages of a VPN and vice versa.
VPN vs Decentralized VPN, How Different Are They and Which is More Secure?
What is a Decentralized VPN?
As a matter of fact, a decentralized VPN conforms to a similar structure as Tor.
Decentralized VPN, also called distributed VPN or blockchain-based VPN, is not controlled by a central server, which is different from a traditional VPN or centralized VPN. Although multiple VPN servers are available around the world, a central VPN server plays a role as a “heart” in the whole system of the virtual private networks. If the central server gets hacked, the whole system will break down.
One significant characteristic of decentralization, however, is that there is no single authority involved. Therefore, the system will naturally be fairer, safer, and more flexible. A decentralized blockchain-based VPN integrates mass traffic of numerous computers and carries out peer-to-peer communication. Therefore, decentralized P2P VPNs don’t have to worry about the threat of being hacked, since there are so many servers available and they’re distributed in a non-linear fashion.
So, future online security and privacy protection of individuals largely depend on decentralized VPN.
What Benefits Can Decentralized VPN Bring You?
Decentralization allows more people to get involved in the connection process while offering a wide range of benefits over the more conventional centralized network in terms of system reliability, scale, and privacy protection. Specifically, instead of passing through a single point of server, data in a decentralized network is randomly passing through multiple nodes with layers of encryption. This makes it almost impossible to track the origins of the data across the network.
The services a Decentralized VPN provides include:
- P2P Mesh Network;
- Digital Privacy Safeguard;
- No Logging of Any Kind;
- Flexibility and Resilience;
- Secure, Private, and Unstoppable.
Traditional VPN vs Decentralized VPN, a Said-Secure VPN vs a Born-to-be-secure VPN
With traditional VPN compared with decentralized VPN, they are different mainly in the network structure that the former is centralization while the latter decentralization.
As your device gets connected with a centralized VPN server, all the communications will go through the tunnel connecting your device with the Internet with ISP bypassed. Without a VPN used, all your data is transmitted directly from your device to the Internet and based on your IP address, all your online activities are “transparent” to your ISP and any prying eyes. However, if the VPN server is hacked or the VPN service provider wants to know about your online activities, it’s a piece of cake. It’s ordinary that VPN service providers swear that all your data won’t be logged. However, it’s nothing but a mouth promise.
When a decentralized VPN is used, however, there’s no need to worry about the truth of the VPN provider’s promise because a decentralized VPN is born to be a secure VPN. Based on the decentralized network established based on blockchain technology, as your data is transmitted from your device, it’ll be distributed to different servers on the path to the Internet and no one is able to get the complete data. Even if one of the servers gets hacked and the data is leaked, it’s still meaningless since the data only accounts for such a small part that the complete data is still safe.
VPN vs Tor vs Decentralized VPN, Which Can 100% Ensure Your Online Security and Anonymity?
First, compared with centralized and decentralized structures, decentralized structures are more secure because all data can be distributed to different servers so that no one can reach the integrity.
Second, compared with a VPN and Tor browser, a VPN is recommended because a VPN works on all your contacts with the Internet no matter where they occur, either on a browser or an application. Moreover, a VPN runs much faster than the Tor browser.
To sum up, to protect your cybersecurity and privacy on the Internet, what you really need is a combination of a VPN plus a decentralized structure, which is decentralized VPN.
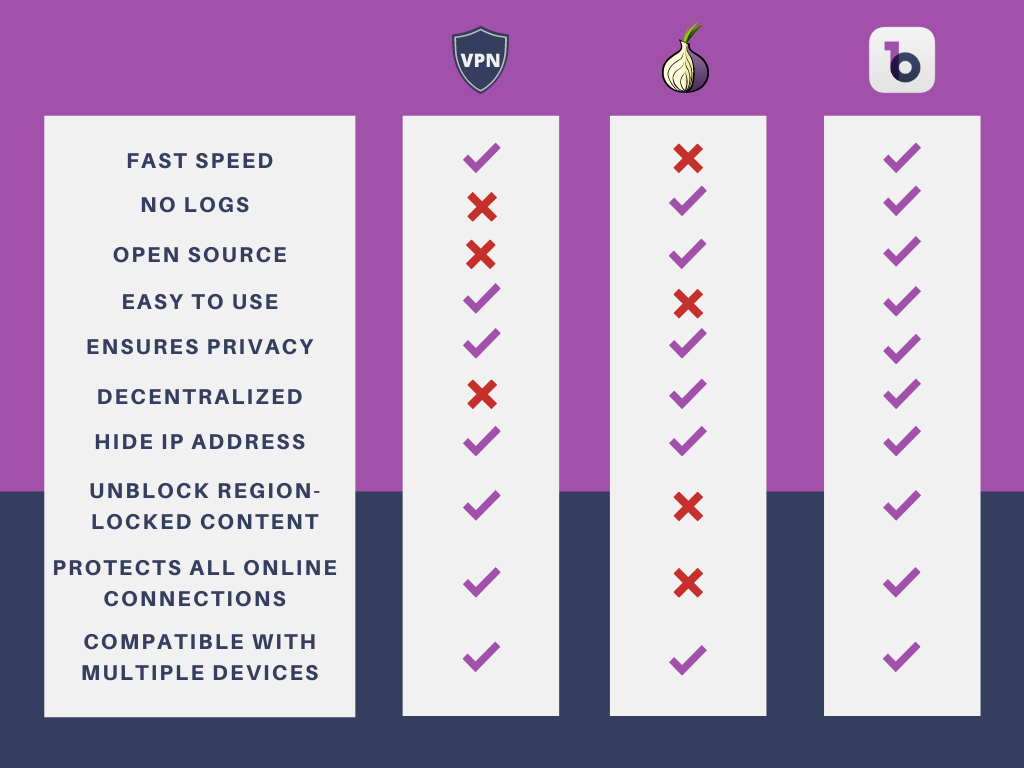
A table can be summarized below on the comparison of VPN vs Tor vs Decentralized VPN.
- How to Tell if Someone is Spying on My Phone and How to Stop That
- Ask Your Employees These Questions to Easily Test Their Cybersecurity Awareness
- What’s Computer Hacking and How to Prevent It
- What is Ransomware? Everything You Should Know About Top 1 Possible Cyberattack in 2021
- Affected by Facebook Leak? How to Stay More Private on Social Media
